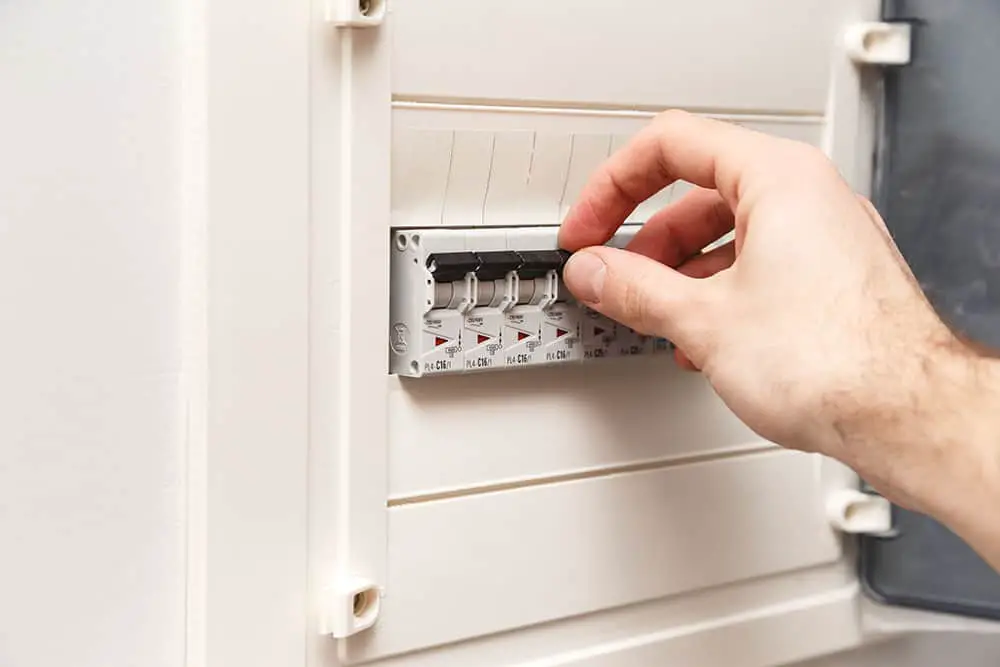
The breaker box of a house is where the circuit breaker panel is located. This is in effect a large switch for the power supply to your home. It helps to keep the electrical current running through your house safe.
The breaker box also contains smaller switches too, that control more specific locations inside your house.
These are known as individual breakers and are designed to add safety precautions to your home.
Breaker boxes generally tend to be either 100 or 200 amps. The size depends on how much electricity is running through the house and the number of circuits you need on the main circuit breaker panel.

Contents
What Can You Find Inside a Circuit Breaker Panel?
There are 6 main components found on the panel inside the breaker box. These are the main circuit breaker, single-pole breaker, double-pole breaker, arc fault circuit interrupters, sub-panels, and bus bars.
The main breaker is the central switch. This controls the flow of electrical current throughout the breaker box.
This will ‘trip’ if the circuit becomes overwhelmed and this causes the electrical current to stop. This could be due to the circuit being overwhelmed or too many electrical appliances being run at once.
The single and double-pole breakers are the two types of sub-breakers. The single-pole breakers tend to be 15-20 amps.
They can handle voltages of up to 120 and are found in most circuits.

Double-pole breakers can be found in a wide range of amps and tend to be able to cope with up to 240 volts.
They are often found for large home electrical items, for instance ovens, washing machines, and air conditioners.
An arc fault circuit interrupter is an additional safety precaution installed in most breaker boxes. These are meant to protect the homeowner from electrocution and electrical fires.
Sub-panels are smaller breaker boxes included within the larger one. These are there to hold more circuits when you do not really have the necessary space available.
Bus bars are the things the two main rows in the circuit breaker panel connect to.
They conduct the electrical current from the main breaker to branching circuits. In other words, this enables the current to reach your electrical outlets.
Why is a Breaker Box Important?
The breaker box contains many safety features to ensure the mains electrical supply does not overpower your home systems.

Without a breaker box, you are exposed to many electrical hazards, shocks, fires, and burns.
The panel inside the breaker box protects the wiring from becoming overloaded or too hot.
How do You Know When You Need to Replace Your Breaker Box?
Generally speaking, a high-quality breaker box can last for around 25-30 years before it will need to be replaced.
Keep an eye out for any of these things though, as they can indicate that your breaker box needs replacing prematurely.
If the circuit breaker keeps tripping regularly, or if it will not reset, it is likely that it needs replacing.
If you notice that the materials and electrical components are overheating, this is also a good indication that the breaker box is on its last legs.
You may also notice a burning smell, or actual material damage to the breaker box components. If you see these, please replace the breaker box immediately.
What to Know Before Playing with the Breaker Box
You should always ensure that you have dry hands and a dry surface to work with before you touch anything electrical. This reduces the risk of electrical shock or any other hazards.
We suggest flipping the switch to test the different areas of the home controlled by the breaker box. This will mean that you know which switches are causing issues.
If your circuit breaker will not reset, please do not keep trying and instead contact a qualified electrician.
Likewise, do not touch any wires that are exposed or damaged. Leave this to the professionals, as it can be very dangerous if you do not know what you are doing.
Do not connect your generator to the breaker box without an approved transfer switch. You should also not connect a generator to a washing machine/dryer outlet.
How do You Wire a Generator to a Breaker Box?
If you are attempting this, we suggest using it as a backup power source in case of a power outage.
Your first step is to isolate the most vital household appliances that need to be run. These could be lights, TV, fridge/freezers, and stoves.
Check the power rating of your generator – a 3500W one should be able to handle these appliances for around 12 hours per tank of fuel.
Check the wattage of the appliances you wish to run and ensure the two figures are compatible.
Choose a wiring system to use, the 2 most common are interlock kits and manual transfer switches.
You should check with the proper authorities to ensure the method you are using is legal in your area.
Next, you will need to install an inlet box hookup on the exterior of your house.
This will be connected to a recessed male connector and this should be compatible with the panel system on the interior of your home.
We recommend consulting a professional to do this for you.
Locate the generator as far away from your house as the cable allows. Plug it into the hookup, matching the holes on the generator cord to the hookup. Turn it around 15 degrees to connect correctly.
Connect the attachment cable from the house to the generator. Select the desired voltage and turn 15 degrees to connect fully.
Ensure the engine throttle is in the right place and there is sufficient oil. Depending on where you live, you may need to preheat the engine.
Turn on the generator and go to your breaker box. Turn off the main utility switch and turn on the generator one.
Flip the breakers individually to ensure the different systems all work correctly. Return to the utility power source,